Artificial intelligence in gaming has entered a new era, moving beyond single-agent mastery to embrace true collaboration between AI agents. The latest research and product launches from Google DeepMind, such as SIMA and Genie 3, have showcased the immense potential of AI world model gaming. These models are not just about creating smarter opponents; they are about enabling AIs to work together, perceive their environments more deeply, and adapt dynamically to new challenges.

Redefining Game Intelligence: From Solo Agents to Team Players
The traditional approach to AI in games focused on building agents that could outperform humans in isolated tasks or specific titles. However, this paradigm is evolving rapidly. The introduction of SIMA (Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent) by Google DeepMind marks a significant leap forward. Rather than optimizing for superhuman skill in one environment, SIMA is designed as a cooperative companion across a spectrum of 3D games. It learns from visual input and natural language instructions, adapting its behavior without direct access to the underlying game code.
This flexibility is crucial for modern gaming environments where unpredictability and player creativity reign supreme. By leveraging SIMA’s generalist capabilities, developers can create more engaging experiences where AI partners understand context and respond intelligently, whether exploring alien worlds or solving puzzles alongside human players.
World Models: The Foundation of Collaborative AI
At the heart of these advances lies the concept of an AI world model. Unlike rule-based bots or narrow neural networks, world models like Genie 3 generate richly interactive virtual environments on demand. Genie 3’s ability to synthesize diverse scenarios allows AIs to train across countless edge cases, expanding their capacity for adaptation and teamwork.
Genie 3 is not just a simulation tool; it acts as an ever-evolving sandbox where multiple agents can learn together. For example, two AIs might collaborate by sharing environmental observations, planning joint actions, or even teaching each other new strategies based on world feedback. This is a radical departure from prior models that treated each agent as an island unto itself.
The Mechanics of Collaboration: How Two AIs Think Together
The technical leap enabling this collaboration comes from innovations like the Herd’s Eye View (HEV) model. HEV aggregates perception data from multiple agents into a shared global perspective, effectively giving each participant access to information they could not observe alone. In competitive benchmarks such as the Pommerman Challenge (where two-agent teams must cooperate with limited communication), this approach has yielded marked improvements in coordination and task success rates.
Key Benefits of Collaborative AI World Models in Games
-

Enhanced adaptability across diverse environments: Models like Google DeepMind’s SIMA can generalize skills and follow instructions in a wide range of 3D game worlds, adapting to new challenges without needing game-specific programming.
-
Improved multi-agent coordination: Collaborative frameworks such as the Herd’s Eye View (HEV) model enable AI agents to share perspectives, resulting in more effective team strategies and decision-making in complex game scenarios.
-

Greater realism and immersion for players: By leveraging world models that allow agents to understand and interact with environments in human-like ways, games can offer more authentic co-op experiences and dynamic NPC behaviors.
-

Efficient training and benchmarking: Platforms like the Pommerman Challenge provide standardized environments for evaluating and improving collaborative AI agents, accelerating research and real-world deployment.
-

Robustness to limited information and communication: Collaborative world models help agents perform well even when information is incomplete or communication is restricted, reflecting real-world multiplayer game constraints.
By combining advanced perception with shared planning frameworks, these systems enable two or more AIs to:
- Dynamically allocate roles based on real-time needs
- Share knowledge about hidden threats or objectives
- Solve complex puzzles that require multi-step cooperation
- Learn from each other’s successes and failures
- Create emergent behaviors that surprise even their developers
This collaborative framework is not limited to academic experiments, it is being actively deployed in commercial titles and research sandboxes alike. As these technologies mature, we can expect richer co-op experiences where both human players and AI partners grow together over time.
What does this mean for the future of AI-driven gaming? First, it signals a shift in how developers and players alike perceive the role of artificial intelligence. Rather than simply facing off against an AI opponent, gamers can now expect to interact with agents that truly understand context, adapt to evolving strategies, and even anticipate the needs of their teammates. This is evident in the way DeepMind SIMA game AI leverages natural language processing and visual comprehension to follow nuanced instructions, whether fetching resources in “No Man’s Sky” or supporting survival efforts in “Valheim. “
Meanwhile, world models like Genie 3 are pushing boundaries by enabling rapid prototyping of new environments and scenarios. This not only accelerates AI training cycles but also democratizes access to advanced simulation tools for indie developers and large studios alike. The result is a more diverse ecosystem of games where collaborative AI can be tailored to various genres, from tactical shooters and open-world adventures to real-time strategy titles.
Challenges Ahead: Balancing Autonomy and Human Experience
Of course, integrating two or more sophisticated planning agents into a single game environment brings new design challenges. Developers must strike a careful balance between autonomous decision-making and player agency. Too much independence from AI partners can lead to unpredictable or frustrating outcomes; too little, and the experience risks becoming stale or overly scripted.
The most promising solutions blend adaptive autonomy with transparent communication channels, both between AIs themselves and with human players. For example, an effective collaborative agent might proactively explain its intended actions or seek confirmation before executing complex maneuvers. As world models grow more robust, expect richer interfaces where players can shape AI behavior through dialogue, gesture, or even in-game demonstrations.
Looking Forward: The Next Generation of Collaborative Game Agents
The trajectory is clear: collaborative AI in games will become increasingly central to both gameplay innovation and narrative depth. We are already seeing early adoption in competitive benchmarks like the Pommerman Challenge, a proving ground for next-level teamwork under tight constraints (details here). As these techniques mature, expect them to filter into mainstream titles where every NPC or co-op companion could be powered by a unique blend of world modeling and real-time collaboration.
Upcoming Games Rumored to Use Next-Gen Collaborative AI
-

No Man’s Sky – Hello Games is reportedly experimenting with DeepMind’s SIMA as an in-game co-op AI companion, enabling players to interact with a generalist agent that can follow natural language instructions and assist with exploration and resource management.
-
Valheim – Rumors suggest that Valheim is among the titles where SIMA has been tested, allowing AI agents to join multiplayer sessions, help with base-building, and adapt to player strategies in real time.
-
Minecraft – With its open-ended gameplay, Minecraft is a prime candidate for collaborative AI integration. Reports indicate that DeepMind’s SIMA has been trialed to enable AI agents that understand player goals and provide dynamic assistance in creative and survival modes.
-
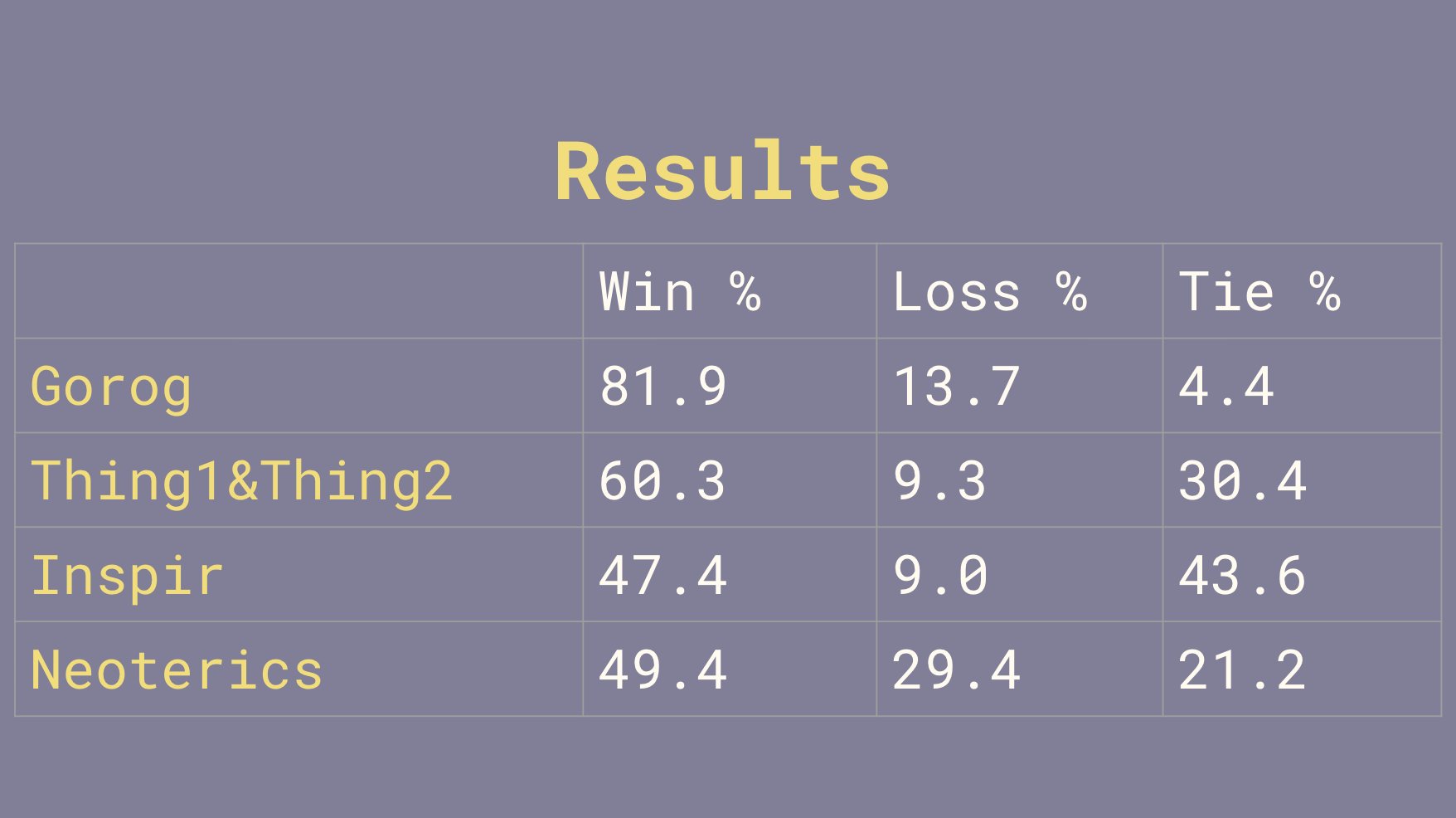
Pommerman Challenge – While not a commercial game, the Pommerman Challenge is a widely recognized benchmark for multi-agent collaboration. The competition is leveraging next-gen AI models to test and refine cooperative agent behaviors in a real-time, adversarial environment.
-

Open World Sandbox Titles (Unannounced) – Industry analysts have noted that several yet-to-be-announced open world games are in talks to integrate Genie 3, DeepMind’s new world model, to generate interactive environments and train collaborative AI agents for richer emergent gameplay.
For developers seeking an edge in AI planning agents games, now is the time to explore these new toolkits. For players, this era promises smarter allies who learn alongside you, and adversaries who challenge you at every turn not just as individuals but as coordinated teams.
The age of isolated bots is ending; the dawn of truly collaborative game intelligence has arrived.



